Use-Case Scenarios
Our app smartly schedules EV charging at optimal times to reduce costs, aligning charging sessions with off-peak hours or when renewable energy is most available.
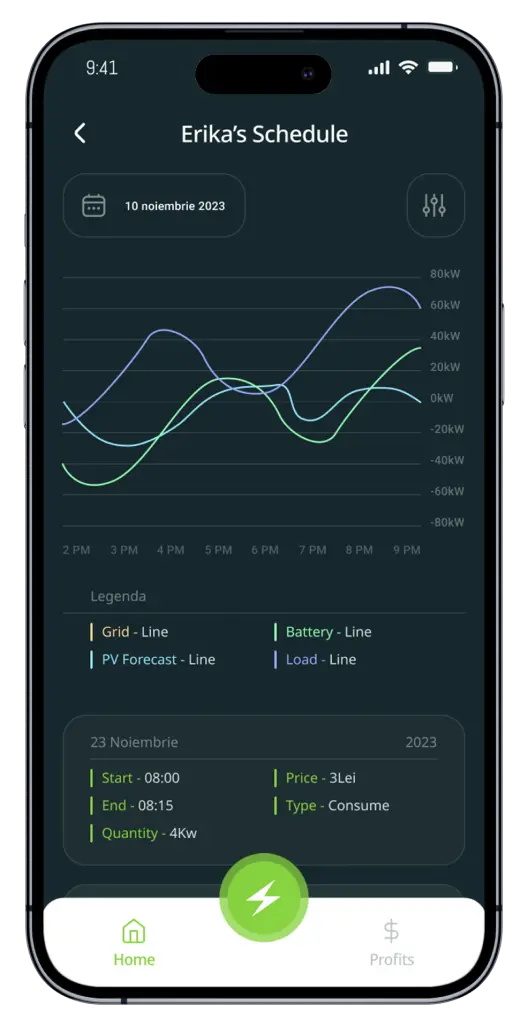
Easily manage your solar generation and battery storage within our app. Utilize surplus energy for personal use or trade it within your community to maximize savings, ensuring you get the most from your solar investment.
Our app enables commercial sites to achieve energy independence by controlling PV systems, storage units, and smart grid functions, ensuring continuous operation even during outages and reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
We empower communities to harness solar and wind energy collectively, enabling peer-to-peer energy trading. Our app creates resilient, localized energy systems, promoting sustainable practices and reducing dependence on centralized grids.
Grid operators deploy advanced grid technologies, including smart grids, to enhance reliability and accommodate renewable energy sources. Real-time monitoring and control ensure efficient energy distribution and reduce environmental impact.
Large-scale industries can use our app to optimize renewable energy integration with wind and solar, balancing supply and demand while maintaining operational efficiency and reducing energy costs.
Our app smartly schedules EV charging at optimal times to reduce costs, aligning charging sessions with off-peak hours or when renewable energy is most available.
We empower communities to harness solar and wind energy collectively, enabling peer-to-peer energy trading. Our app creates resilient, localized energy systems, promoting sustainable practices and reducing dependence on centralized grids.

Easily manage your solar generation and battery storage within our app. Utilize surplus energy for personal use or trade it within your community to maximize savings, ensuring you get the most from your solar investment.
Grid operators deploy advanced grid technologies, including smart grids, to enhance reliability and accommodate renewable energy sources. Real-time monitoring and control ensure efficient energy distribution and reduce environmental impact.
Our app enables commercial sites to achieve energy independence by controlling PV systems, storage units, and smart grid functions, ensuring continuous operation even during outages and reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
Large-scale industries can use our app to optimize renewable energy integration with wind and solar, balancing supply and demand while maintaining operational efficiency and reducing energy costs.